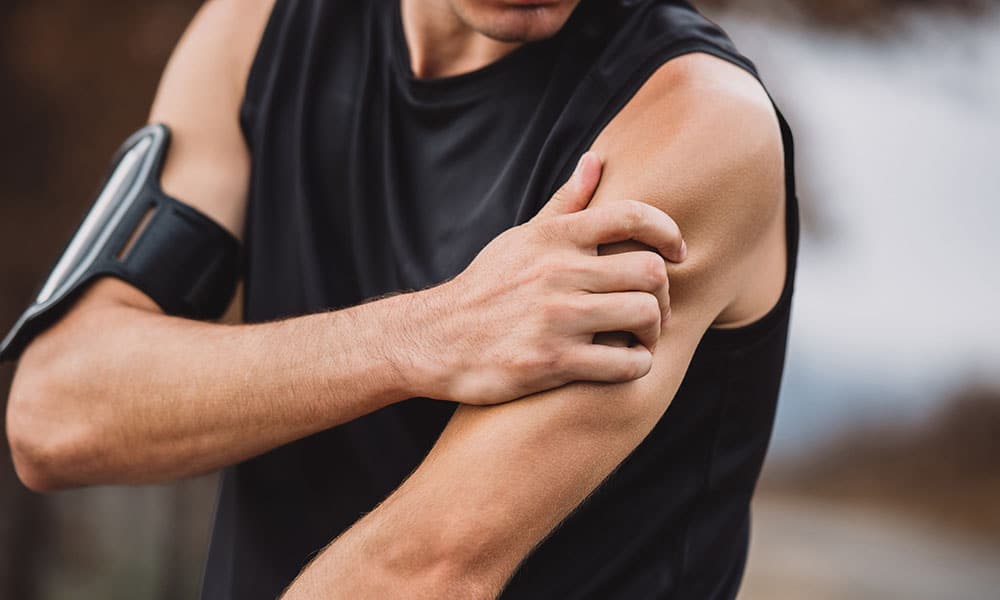
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, is a prevalent ailment affecting millions of people worldwide. Tennis elbow, despite its name, is not confined to sports; it may affect anybody who often utilises their forearm muscles. In this detailed guide, we’ll look at tennis elbow’s causes, symptoms, and remedies.
Tapentadol 200mg is a larger dose of the medicine used to treat moderate to severe pain. Tapentadol 200mg, like the 100mg dosage, is an opioid analgesic. Its mode of action includes binding to the mu-opioid receptor and blocking norepinephrine reuptake, resulting in dual pain relief benefits.

What is tennis elbow?
Tennis elbow is a kind of tendinopathy that is defined by inflammation or degeneration of the tendons around the lateral epicondyle of the humerus bone in the elbow. These tendons link the forearm muscles to the bony prominence outside the elbow. Repetitive actions and tension on the tendons usually cause the ailment to develop progressively over time.
Causes of Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow is often connected with sports requiring repeated arm motions, such as tennis, thus the name. However, it may be induced by several different activities or jobs, such as:
Overuse: Engaging in repeated actions, such as grasping, twisting, or lifting, without enough rest, may strain the elbow tendons and cause tennis elbow.
activities: In addition to tennis, activities requiring repeated arm motions such as golf, squash, and racquetball may contribute to the development of tennis elbow.
Occupational Factors: Jobs requiring repeated hand and wrist motions, such as carpentry, plumbing, painting, or typing, increase the likelihood of developing tennis elbow.
Age and gender: Tennis elbow may develop at any age, although it is more frequent in those aged 30 to 50. Furthermore, males are somewhat more likely to develop tennis elbow than women.
Tapentadol 100mg is a medicine used to relieve moderate to severe pain. It is an opioid analgesic. The major method of action is to bind to the mu-opioid receptor and impede norepinephrine reuptake. This multimodal mechanism helps manage pain by influencing both the opioid and noradrenergic pathways.
Symptoms of tennis elbow
Recognising the signs of tennis elbow is critical for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common indications and symptoms include:
discomfort: Persistent discomfort on the outside side of the elbow, which may spread down the forearm.
Weak Grip Strength: Difficulty holding things or doing basic activities owing to weak forearm muscles.
Tenderness and sensitivity to touch at the bony protrusion of the elbow.
Stiffness in the elbow joint, particularly after periods of inactivity or after getting up in the morning.
Difficulty in Extension: Difficulty completely extending the arm, especially while straightening the elbow against opposition.
Treatment Options For Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow is usually managed well by a mix of conservative therapies and lifestyle changes. Some of the most generally advised treatment approaches are:
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that worsen symptoms and providing the afflicted arm enough rest to facilitate recovery.
Ice Therapy: Using ice packs on the afflicted region for 15-20 minutes many times a day will help relieve pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy involves doing particular exercises and stretches to increase flexibility, strengthen forearm muscles, and promote healing.
Bracing or splinting: Using a brace or splint to immobilise the elbow and alleviate tendon tension during activity.
Over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen may help reduce the discomfort and inflammation caused by tennis elbow.
Corticosteroid Injections: In extreme situations when conservative methods have failed, corticosteroid injections may be used to relieve inflammation and discomfort.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT): This non-invasive therapy includes applying shock waves to the afflicted region to promote healing and alleviate discomfort.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP injections, which include concentrated platelets from the patient’s own blood, may speed up the healing process and encourage tissue restoration.
Surgery: In rare situations when conservative therapy fail, surgical intervention may be required to repair or remove damaged tendon tissue.
Buy tapentadol online is a centrally acting analgesic (pain reliever) that treats moderate to severe pain. It is classed as an opioid analgesic and comes in both immediate and extended-release forms. Tapentadol binds to mu-opioid receptors in the central nervous system and inhibits norepinephrine reuptake.
Prevention Strategies
While tennis elbow may be difficult to avoid, particularly in those with predisposed conditions, several precautions might help lower the chance of getting the condition:
good technique: Whether participating in sports or completing occupational duties, using good technique and body mechanics helps reduce elbow strain.
Gradual Progression: When beginning a new activity or workout regimen, gradually increase the intensity and time to enable the muscles and tendons to adjust.
Wearing supporting braces or other ergonomic equipment might help protect the elbow joint during repeated tasks.
Regular pauses: Taking numerous pauses during repeated chores to relax and stretch the muscles may help avoid overuse ailments such as tennis elbow.
Strength and Flexibility Training: Including exercises that improve forearm strength and flexibility in your fitness routine will assist avoid muscular imbalances and lower your chance of injury.
To summarise, tennis elbow is a common musculoskeletal ailment characterised by discomfort and inflammation in the outer region of the elbow. While it may have a substantial influence on everyday activities, there are effective treatment options available to reduce symptoms and aid recovery. Understanding the origins, symptoms, and preventative actions linked with tennis elbow allows people to take proactive efforts to safeguard their elbow health and keep an active lifestyle.

