Cooking

How to Cook Delicious Meals Easily
Effortless Gourmet: Simple Steps to Cook Delicious Meals at Home. Discover the joy of cooking with these simple steps to prepare delicious meals that will impress your family and friends. Whether...
15 Jul 2025

Top 10 Must-Try Recipes for Beginners
Introduction to Cooking for Beginners. Embarking on your culinary journey can be both exciting and a bit daunting. To help you get started, we've compiled a list of 10 must-try recipes that are...
14 Jul 2025

10 Must-Try Recipes for Busy Weeknights
Introduction. Busy weeknights call for quick, delicious, and easy-to-make meals. Whether you're a seasoned chef or a cooking novice, these 10 must-try recipes will save you time and satisfy your...
16 Jul 2025

Easy Recipes for Quick Weeknight Dinners
Simple and Delicious Weeknight Dinner Ideas for Busy Families. Finding time to prepare a nutritious and delicious dinner during the week can be a challenge for many families. With these easy...
16 Jul 2025
Communication
Secrets to Mastering Public Speaking Skills
Introduction to Mastering Public Speaking. Public speaking is an essential skill that can significantly impact your personal and professional life. Whether you're delivering a presentation at work, speaking at a conference, or giving a toast at a wedding, the ability to communicate effectively in front of an audience is invaluable. This article will explore expert tips and strategies to help you master public speaking skills and deliver your message with confidence and clarity.. Understand Your Audience. Before you step onto the stage, it's crucial to understand who your audience is. Tailoring your message to meet their interests, knowledge level, and expectations can make your speech... Read More
14 Jul 2025

Finance

The Ultimate Guide to Personal Finance
Introduction to Personal Finance. Personal finance is a crucial aspect of everyone's life, yet many find it overwhelming. This guide is designed to simplify the complexities of managing your...
15 Jul 2025

Smart Strategies for Investing in Stocks
Introduction to Stock Market Investing. Investing in the stock market can be a lucrative way to build wealth over time. However, it requires knowledge, strategy, and patience. This guide will...
16 Jul 2025

The Role of Machine Learning in Finance
Introduction to Machine Learning in Finance. Machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence, has become a cornerstone in the evolution of the financial sector. By leveraging algorithms and...
20 Jul 2025

The Beginner's Guide to Investing Wisely
Introduction to Smart Investing. Investing wisely is not just about picking the right stocks or assets; it's about understanding the fundamentals of the market, knowing your financial goals, and...
17 Jul 2025
Fitness

5 Effective Strategies for Weight Loss
Introduction. Losing weight can be a challenging journey, but with the right strategies, it's entirely achievable. This article explores five effective techniques that can help you shed pounds and...
15 Jul 2025

The Best Workout Routines for Beginners
Introduction to Beginner Workout Routines. Starting a fitness journey can be overwhelming for beginners. With so many options available, it's hard to know where to begin. This guide is designed to...
15 Jul 2025

How to Stay Fit Without a Gym
Introduction to Staying Fit Without a Gym. In today's fast-paced world, finding time to hit the gym can be challenging. However, staying fit doesn't require expensive equipment or a gym...
17 Jul 2025

The Complete Beginner's Guide to Yoga
Welcome to the World of Yoga. Embarking on a yoga journey can transform your life, offering a path to improved flexibility, strength, and mental clarity. This guide is designed to introduce...
15 Jul 2025
Blogging

How to Start a Successful Blog Today
Introduction to Blogging Success. Starting a blog in 2024 might seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can be a rewarding venture. Whether you're looking to share your passion, establish...
15 Jul 2025

How to Start a Successful Blog Quickly
Introduction to Blogging Success. Starting a blog can seem daunting at first, but with the right approach, you can set up a successful blog quickly. This guide will walk you through the essential...
16 Jul 2025

How to Start a Successful Blog Fast
Introduction to Fast-Track Blogging Success. Starting a blog can seem daunting, but with the right approach, you can launch a successful blog quickly. This guide will walk you through the...
17 Jul 2025
Decor

Easy DIY Home Decor Ideas for Beginners
Simple and Creative DIY Home Decor Projects for Newbies. Embarking on DIY home decor projects can be a thrilling way to personalize your living space without breaking the bank. Whether you're a...
17 Jul 2025

Creative DIY Projects for Home Decor
Transform Your Home with These Creative DIY Projects. Looking to add a personal touch to your home decor? DIY projects are a fantastic way to infuse your space with personality and creativity. Not...
16 Jul 2025

Easy DIY Home Decor Ideas for All
Transform Your Space with These DIY Home Decor Ideas. Looking to refresh your home without breaking the bank? DIY home decor projects are a fantastic way to personalize your space while staying...
15 Jul 2025
Marketing
The Complete Guide to Digital Marketing
Introduction to Digital Marketing. In the ever-evolving digital landscape, mastering digital marketing is crucial for businesses aiming to thrive online. This guide will walk you through the essential strategies and tools needed to excel in digital marketing.. Understanding Digital Marketing. Digital marketing encompasses all marketing efforts that use an electronic device or the internet. Businesses leverage digital channels such as search engines, social media, email, and other websites to connect with current and prospective customers.. Key Components of Digital Marketing. Search Engine Optimization (SEO):. The practice of increasing the quantity and quality of traffic to your website... Read More
15 Jul 2025

Health

How to Improve Your Sleep Quality
Introduction to Better Sleep. Sleep is a cornerstone of good health, yet many struggle to achieve restful nights. Improving your sleep quality can enhance your mood, energy levels, and overall...
15 Jul 2025

The Science Behind Better Sleep Habits
The Importance of Quality Sleep. Quality sleep is foundational to our overall health and well-being. It affects our mood, energy levels, and even our weight. Understanding the science behind...
16 Jul 2025

The Science Behind Effective Weight Loss
Understanding the Fundamentals of Weight Loss. Weight loss is a journey that millions embark on every year, yet many find themselves struggling to achieve lasting results. The science behind...
17 Jul 2025

Biotechnology Breakthroughs That Are Saving Lives
Revolutionary Advances in Biotechnology Transforming Healthcare. In recent years, biotechnology has emerged as a beacon of hope, offering groundbreaking solutions to some of the most pressing...
18 Jul 2025
Technology

Creating Immersive VR Experiences: A Guide
Introduction to Virtual Reality. Virtual Reality (VR) has transformed the way we interact with digital content, offering unparalleled immersive experiences. From gaming to education, VR's...
21 Jul 2025

Robotics in Healthcare: A Game Changer
The Dawn of Robotics in Healthcare. In recent years, the integration of robotics into healthcare has marked a revolutionary shift in how medical services are delivered. From surgical robots to...
18 Jul 2025

Wearable Tech for Athletes: Performance Enhancement
Introduction to Wearable Technology in Sports. In the realm of competitive sports and personal fitness, wearable technology has emerged as a game-changer. These innovative devices are designed to...
19 Jul 2025

Breaking Down AI Myths for Beginners
Introduction to AI Myths. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly evolving field that has captured the imagination of many. However, with its growth, numerous myths and misconceptions have...
19 Jul 2025
Travel

The Best Travel Destinations for 2023
Discover the Best Travel Destinations for 2023. As the world opens up, 2023 promises to be a year filled with unforgettable travel experiences. Whether you're seeking serene beaches, bustling...
15 Jul 2025

Top 5 Travel Destinations for Adventure Lovers
5 Ultimate Adventure Spots for Thrill Seekers. For those who crave excitement and adrenaline, the world is full of incredible destinations that offer unforgettable adventures. From towering...
15 Jul 2025

The Best Travel Destinations for Adventure Lovers
Discover the World's Most Exciting Adventure Destinations. For those who crave excitement and yearn to explore the unknown, the world is full of breathtaking destinations that promise...
16 Jul 2025
Recent Post
Web Development Trends That Will Dominate 2023
Introduction to Web Development Trends in 2023. As we step into 2023, the web development landscape continues to evolve at a rapid pace. With new technologies and methodologies emerging,... Read More
05 Aug 2025

The Challenges of Creating Immersive VR Experiences
Introduction to Virtual Reality Challenges. Creating immersive Virtual Reality (VR) experiences is a frontier that many developers and designers are eager to explore. However, the path to crafting... Read More
05 Aug 2025

Getting Started with Virtual Reality Development
Introduction to Virtual Reality Development. Virtual Reality (VR) development is an exciting field that combines creativity with technology to create immersive experiences. Whether you're a... Read More
05 Aug 2025

The Potential of VR in Education and Training
The Transformative Impact of Virtual Reality on Learning and Skill Development. Virtual Reality (VR) technology has rapidly evolved from a futuristic concept into a practical tool with the... Read More
05 Aug 2025

How VR is Transforming the Gaming Industry
The Revolutionary Impact of Virtual Reality on Gaming. Virtual Reality (VR) has emerged as a groundbreaking technology that is reshaping the gaming industry in unprecedented ways. By offering... Read More
05 Aug 2025
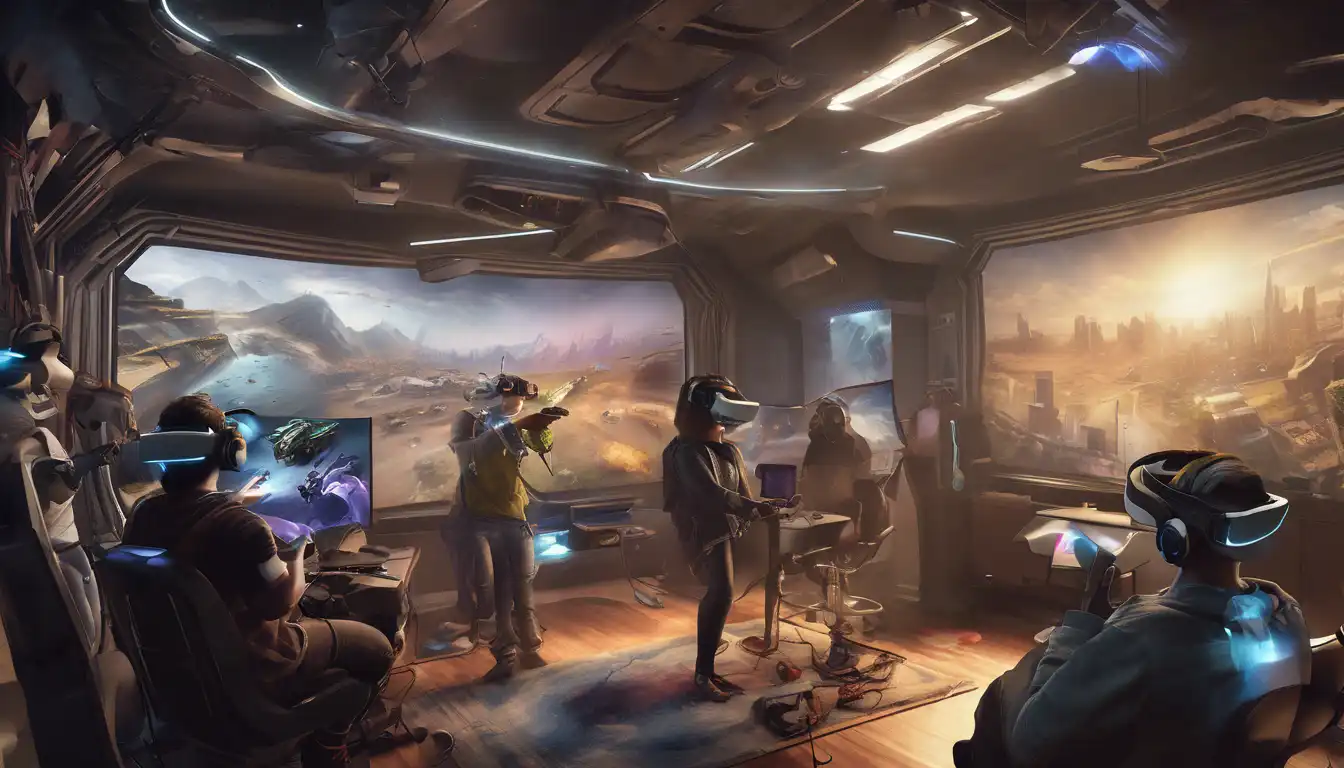

Virtual Reality: The Next Frontier in Tech
Introduction to Virtual Reality. Virtual Reality (VR) is rapidly becoming one of the most exciting and innovative fields in technology today. With its ability to immerse users in a completely... Read More
05 Aug 2025
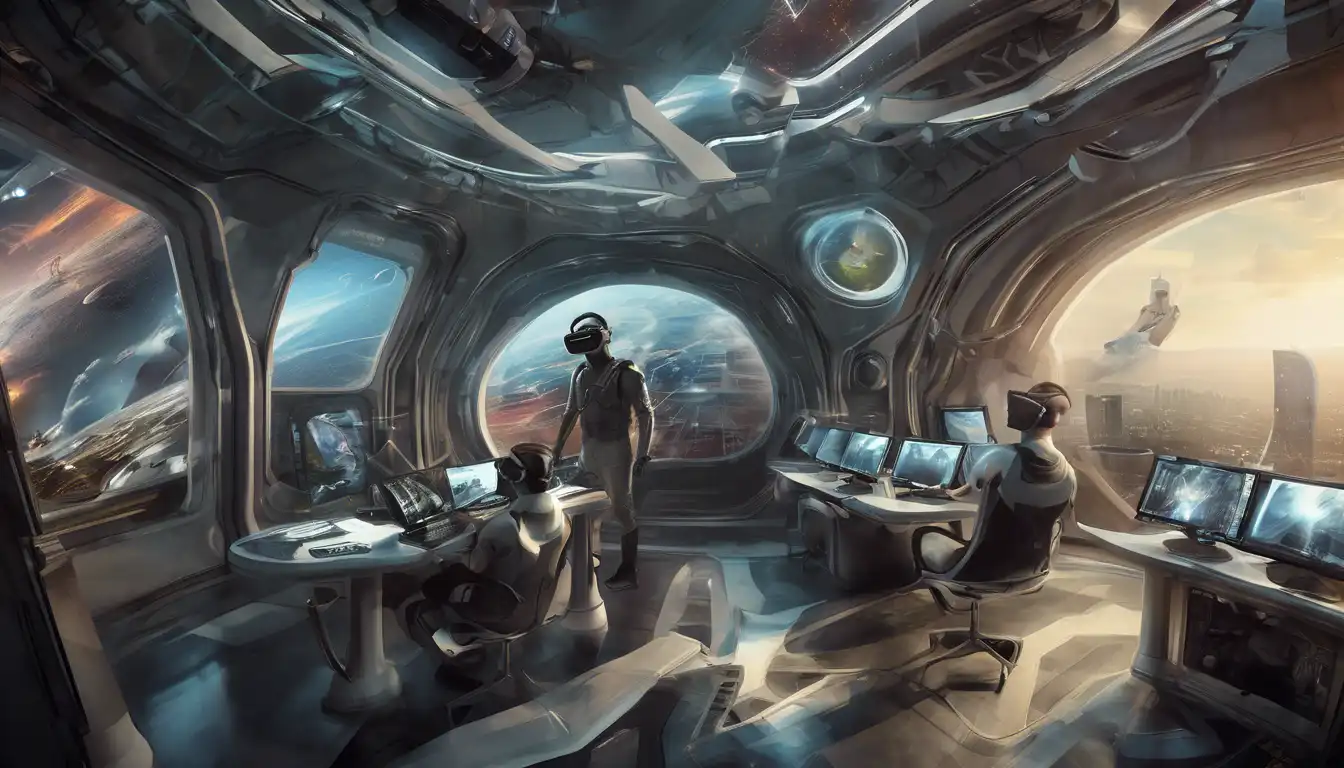

Emerging Trends in Software Development
Introduction to Modern Software Development Trends. The landscape of software development is constantly evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging at a rapid pace. These... Read More
05 Aug 2025

How to Manage Software Development Projects Effectively
Introduction to Effective Software Development Project Management. Managing software development projects effectively is crucial for delivering quality products on time and within budget. This... Read More
05 Aug 2025

The Importance of Code Quality in Software Development
Why Code Quality Matters in Modern Software Development. In the fast-paced world of software development, the quality of code is often overlooked in favor of speed and functionality. However,... Read More
05 Aug 2025

Ethical Considerations in Robotics Development
Introduction to Ethical Robotics. In the rapidly evolving field of robotics, ethical considerations are becoming increasingly paramount. As we stand on the brink of a new era where robots and... Read More
05 Aug 2025
🔥 Popular Posts
- Networking Tools for Troubleshooting Connection Issues 8245 views
- Understanding the Psychology Behind Gaming Addiction 2663 views
- Artificial Intelligence in Everyday Life: What's Next? 1623 views
- How to Start a Successful Blog Quickly 898 views
- How to Start a Successful Blog Fast 893 views
- How to Start a Successful Blog Today 890 views
- Quantum Computing Applications You Didn't Know About 782 views
- Biotechnology Breakthroughs That Are Saving Lives 500 views
- IoT in Healthcare: A Game Changer 269 views
- The Security Challenges of IoT Devices 269 views
- Gadgets That Make Your Home Smarter 269 views
- DevOps: Bridging the Gap Between Teams 269 views
- The Future of Wearable Technology 269 views
- The Future of Hardware: What's Next? 268 views
- Internet of Things: Connecting the World 268 views
- Building a PC: A Beginner's Guide 268 views
- The Best Tech Gadgets for Productivity 268 views
- How Smart Gadgets Are Changing Our Lives 268 views
- DevOps Culture: Collaboration and Efficiency 268 views
- Cybersecurity Threats You Can't Afford to Ignore 268 views